PedAMINES app for iPhone and iPad
Developer: HUG Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève
First release : 07 Mar 2018
App size: 0 Bytes
PedAMINES™ is the first drug dose calculator which can be used for either continuous intravenous infusions or bolus drugs preparation, and which has been scientifically validated (1). This app is designed to support nurses and physicians step-by-step from order to delivery of an infinite range of drugs in real time. It has been developed by medical computer scientists and pediatric emergency physicians.
PedAMINES™ is suitable for use in emergency medicine, critical care, anesthesia, onco-hematology, veterinary medicine, and many other medical fields in university hospitals, rural hospitals, clinics, and humanitarian organizations in remote areas.
PedAMINES features :
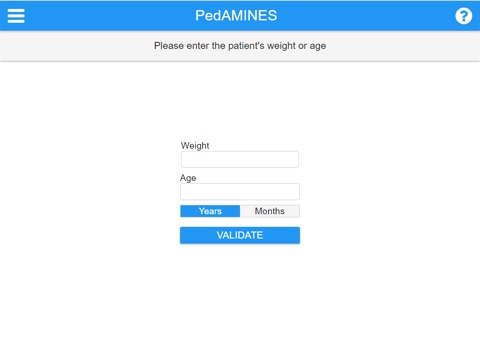
Automatic age or weight-based drug dose calculation.
Calculation of infusion rates in mL/h based on various rate units (mcg/kg/min, mcg/kg/h, UI/kg/h, mg/kg/h).
Calculation of bolus doses in absolute dose (mg) or volume (mL) based on weight-based dosages (mg/kg).
Fully customizable drugs database.
In-app drug editor allow to create, expand and customize your drug list according to your own needs and local drug habits.
Keep full control over the app by determining the drug concentration, starting dose, dosage increments, infusion ranges, type of diluent, initial infusion rate, and maximal dose.
Interact with the app in real-time.
The drug preparation sequence is detailed step-by-step.
Multiple drugs can be prepared and run in parallel.
Reduces stress and cognitive workload.
Use an intuitive and ergonomic-based interface with reactivity and autonomy.
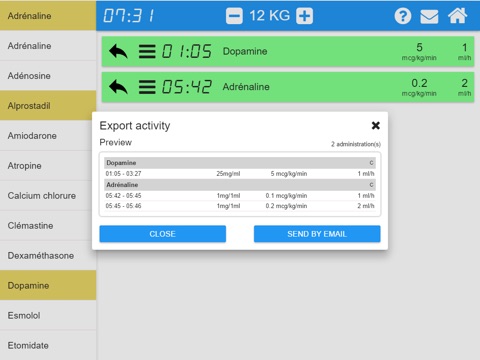
Keep historic files of all actions performed.
Print a complete and detailed report of all actions performed.
No internet connection is required.
(1) PedAMINES was shown to reduce time to drug preparation by 58%, time to drug delivery by 45%, and medication errors from 70% to 0% when compared with conventional methods (ref : J Med Internet Res 2017;19(2):e31. PMID: 28148473).